Abstract
Background: Mutations in the pre-mRNA splicing factor SF3B1 are now established as one of the classification criteria in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and their presence constitutes a disease subset with distinctive biological features, clinical outcomes and prognosis. Mutation sites map preferentially in the HEAT domains of the C-terminal region of the protein with K700E accounting for more than 50% of all mutant cases. Specific clinical phenotypes may be associated with the various mutational SF3B1 hits. In human and murine models, K700E impairs pre-mRNA splicing and hematopoiesis. In other cancers, R625 and K666 mutations lead to deregulated splicing mostly affecting the use of alternative 3′ splice sites. We investigated whether the presence of specific SF3B1 amino-acid alterations and concurrent mutations resulted in distinct downstream effects with clinical implications in a cohort of patients (pts) with myeloid neoplasms (MN).
Methods: We analyzed a cohort of 2134 cases derived from pts diagnosed with MN using Next Generation Sequencing techniques (whole exome/targeted/Sanger sequencing) on bone marrow (BM) and/or peripheral blood specimens. We identified SF3B1 mutations in 7% (143/2134) of the samples. Clinical characteristics included but were not limited to: blood counts, cytogenetics, percentage ring sideroblasts (RS), IPSS-R, treatment received (erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESA), lenalidomide (LEN), and hypomethylating agents (HMAs)), treatment response per International Working Group criteria, and last follow up/death. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from date of initial diagnosis till date of last follow up/death.
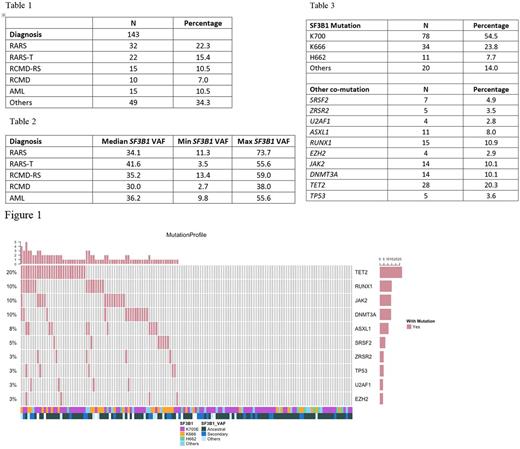
Results: The SF3B1 mutated cohort (N=143) had a median age of 67 yrs (range, 11-93), a median follow up of 1 yr and 48% female. The most common diagnoses were Refractory Anemia with Ring Sideroblasts (RARS, 22%) and RARS with thrombocytosis (RARS-T, 15%) (Table 1). The mean WBC count was 8.4 x 109/L, ANC was 4.3 x 109/L, platelet count was 238 x 103/μL, hemoglobin level was 9.5 g/dL and BM blast percentage was 10%. The mean RS % was 26% (range, 0-85). Pts with normal karyotypes constituted 55% (79/143). The median OS was 71 months (82 months for MDS pts). Among the 21 distinct nonsynonymous mutations, the most common were substitutions K700E (54.5%) and K666 (24%) (Fig. 1). Median SF3B1 VAF (variant allelic frequency) was the highest in RARS-T (42%) followed by AML (36%) and RCMD-RS (35%) (Table 2). Cross-sectional mutational analyses showed that TET2 was the most common co-mutation (20%) followed by RUNX1 (11%) (Table 3). There was a significant difference in the distribution of the different SF3B1 mutations among the disease subgroups, with K666 mutations not being detected in RCMD with and without RS (Fisher's Exact Test, P= .009). In multivariate Cox Regression analyses, after adjustment for age, sex, cytogenetics and SF3B1 VAF, JAK2 co-mutation was significantly associated with a better OS (P= .033, HR=6.135, 95% CI: 1.158-32.5) while mutated TP53 was significantly associated with a worse OS (P < .001, HR=0.004, 95% CI: 0.001-0.036).
MN pts harboring SF3B1 mutations at H662D/Y/Q (8%) in the absence of other co-mutations had a lower response to therapy (ESA, LEN, HMAs) as compared to pts with other SF3B1 mutations (P= .028). When response to LEN was assessed separately in this cohort, SF3B1 mutation at H662 showed a significantly lower response at 16 weeks from initiation of LEN (P= .022).
Conclusion: Single codon SF3B1 mutations may influence the clinical phenotypes of pts with MN and may help guide clinical decisions regarding choice of therapy and prediction of response to therapy. We found that clinical response to treatment is lower with H662 mutations as compared to other SF3B1 mutations. Determining the molecular mechanism of this lower response to therapy in this particular subset of SF3B1 mutated pts may have an impact on our treatment approach.
Advani: Takeda/ Millenium: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy. Gerds: CTI BioPharma: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy. Carew: Millenium/ Takeda: Research Funding. Sekeres: Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.